In today’s post, we will study the topic of “What is Cell Division Class 9th”, why it is so important, and what roles it plays in our bodies. What is it that keeps our bodies running?
What is cell division class 9th?
One essential biological process for the development, upkeep, and reproduction of organisms is cell division. It performs a number of vital functions, such as stimulating growth and development, replenishing damaged, aged, or dead cells, and aiding in the creation of gametes, which are required for reproduction.
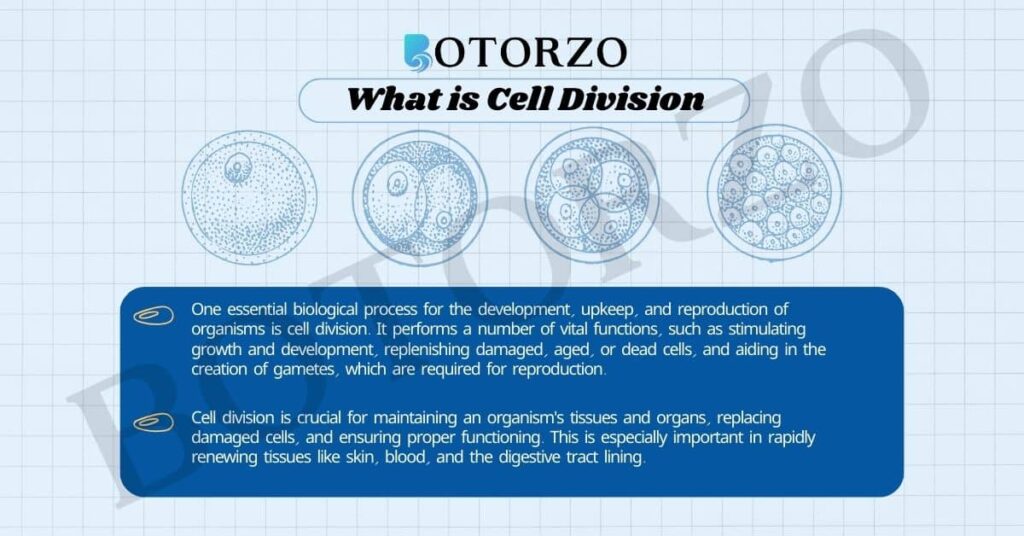
Growth and development are two main drivers of the formation of new cells. Multicellular organisms need more cells to support their growing functional and structural needs as they get bigger and more complex. Through the process of cell division, identical daughter cells can be produced, enabling the organism to grow to its maximum size and complexity.
Cell division is crucial for maintaining an organism’s tissues and organs, replacing damaged cells, and ensuring proper functioning. This is especially important in rapidly renewing tissues like skin, blood, and the digestive tract lining.
Additionally, cell division, specifically meiosis, is vital for sexual reproduction, producing specialized gametes (sperm and eggs) with half the genetic material. When these gametes unite during fertilization, they create genetically diverse offspring, contributing to species continuity. In summary, cell division, encompassing mitosis and meiosis, is fundamental for growth, repair, and reproduction in organisms.
Why is cell division necessary?
The growth, repair, and reproduction of an organism all depend on cell division. Growth and tissue maintenance are made possible by mitosis, which produces daughter cells that are genetically identical to the mother cell and have the same number of chromosomes.
It is also essential for the rapid renewal of tissues such as the lining of the digestive tract and skin, where it replaces old, damaged, or dead cells. Meiosis also guarantees that gametes with half as many chromosomes are formed, which promotes genetic diversity in progeny during sexual reproduction. In conclusion, cell division is an essential process that keeps organisms alive and well.
- Read Structure Of Cell: Plasma Membrane, Nucleus, Cytoplasm And Organelles
- Cell Organelles With Its All Parts
- Cell Organelles: Detailed Images With All Parts (CLASS 9)
Cell Division Importance
We will read about the Cell Division Importance. The points given below tell us about the Cell Division importance in our body. By reading all the points, you can know its importance for us and what functions it performs for our body.
- Cell division is crucial for an organism’s growth and development.
- Mitosis, a form of cell division, produces daughter cells that are genetically identical to the mother cell.
- Mitosis ensures the continuity of the same number of chromosomes in daughter cells.
- Cell division is essential for the maintenance and repair of an organism’s tissues and organs.
- Rapidly renewing tissues like the digestive tract and skin depend on cell division to replace old, damaged, or dead cells.
- Tissue renewal is vital for maintaining proper organ and body function.
- Mitosis plays a key role in preserving genetic stability within an organism.
- Meiosis, another form of cell division, is dedicated to sexual reproduction.
- Meiosis results in the formation of gametes, such as sperm and eggs.
- Gametes produced by meiosis have half the number of chromosomes compared to other cells.
- This reduction in chromosome number promotes genetic diversity in offspring during sexual reproduction.
- Genetic diversity is crucial for species adaptation and evolution over time.
- The process of cell division allows for the formation of new, healthy cells.
- It ensures the continuity and well-being of organisms by replacing damaged or dead cells.
- In summary, cell division is an essential process that sustains life, allowing organisms to grow, repair, and reproduce.
types of cell division
• Mitosis
• Meiosis
There are two primary types of cell division: mitosis and meiosis, each serving distinct but crucial purposes in the life of an organism.
Mitosis:
Mitosis is a type of cell division that occurs in somatic (body) cells. Its primary purpose is to produce two identical daughter cells, each with the same number of chromosomes as the parent cell. The process is essential for growth, tissue repair, and asexual reproduction in some organisms. Mitosis consists of a single division that results in two diploid (2n) daughter cells, and it plays a crucial role in maintaining the overall stability and integrity of an organism’s genetic material.
Meiosis:
Meiosis is another type of cell division that occurs in germ cells (sperm and egg cells) and is involved in sexual reproduction. Unlike mitosis, meiosis consists of two successive divisions: meiosis I and meiosis II. The main purpose of meiosis is to reduce the chromosome number by half, resulting in four non-identical haploid (n) daughter cells. This reduction in chromosome number is critical in sexual reproduction, as it ensures genetic diversity and contributes to the uniqueness of offspring. Meiosis is responsible for the creation of gametes (sperm and egg cells) in animals and spores in plants and fungi.
Read Engineering
f.a.q’s
What is cell division?
Cell division is a fundamental biological process essential for the development, maintenance, and reproduction of organisms.
What are the main functions of cell division?
Cell division serves crucial roles in promoting growth and development, replacing damaged or dead cells, and aiding in the creation of gametes for reproduction.
What is the role of mitosis in cell division?
Mitosis is responsible for growth and tissue maintenance, producing genetically identical daughter cells that maintain the same number of chromosomes as the mother cell.
Why is cell division important for tissue maintenance?
Cell division, especially in rapidly renewing tissues like skin, blood, and the digestive tract lining, replaces old, damaged, or dead cells, ensuring proper tissue functioning.
How does meiosis contribute to sexual reproduction?
Meiosis produces specialized gametes, such as sperm and eggs, each with half the genetic material, promoting genetic diversity in offspring during sexual reproduction.
why the number of chromosomes is reduced to half in the daughter cell in meiosis cell division
The reduction in chromosome number by half in daughter cells during meiosis ensures genetic diversity in offspring during sexual reproduction, promoting species adaptation and evolution over time.
Why is genetic diversity in offspring important during sexual reproduction?
Genetic diversity resulting from meiosis is crucial for species adaptation and evolution over time.
How do mitosis and meiosis differ in their chromosome numbers?
In mitosis, daughter cells have the same number of chromosomes as the mother cell, while in meiosis, daughter cells have half the number of chromosomes compared to the mother cell, ensuring genetic diversity in the latter.

